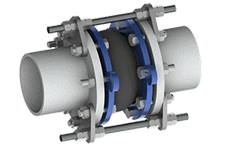
Multi-Purpose PTFE (Teflon®) Lined Expansion Joints
Solid molded PTFE expansion joints are made to withstand high pressures and temperatures in a compact, space-saving design. They are light-weight and corrosion and chemical-resistant, and are available in both Rubber and Metal configurations.
PTFE (Teflon®) is a synthetic fluoropolymer which finds numerous applications due to its non-stick nature, thermal stability, and high resistance to chemicals. Elastomeric covering on solid PTFE and PTFE-lined metallic Expansion Joints are designed for environmentally corrosive applications. A Kevlar® reinforcement overlay can be used to increase working pressures and provide additional safety factors for PTFE Expansion Joints.
Benefits of PTFE Lined Expansion Joints
- High resistance to corrosion
- High resistance to chemicals
- High thermal stability
- Short face-to-face dimensions – ideal for installation where space limitations are a factor
- Elastomeric (Viton®, EPDM, Neoprene) and metal covers available
- Simple retrofit into existing piping systems
- Cost effective solution to compensate for movement in piping systems
OTHER TYPES OF EXPANSION JOINTS:
Formed PTFE Style Expansion Joints
Style 112
Style 113
Style 115
Multi-purpose PTFE expansion joints can operate with full vacuum to 160 PSI depending on the type and number of convolutions.. These types of expansions joints are typically used with highly corrosive medias, with glass or plastic piping, or in heating, ventilating, and air conditioning applications where space is at a premium.
Lightweight and corrosion-resistant.
SecureFlex Peroxide-Cured EPDM & Kevlar® Reinforced Single and Double Arch Expansion Joints
- Molded and vulcanized in hydraulic presses for a smooth finished product
- Single, double, concentric and eccentric construction available
- Available in Viton®, EPDM, Butyl, Pure Gum and Nitrile
- Flanges are laser cut from carbon steel and other available alloys
Dura-Perm Combined Technology PTFE and Rubber Expansion Joints
- The excellent chemical resistance of PTFE
- The flexibility of rubber expansion joints
- Thermal stability
- Anti-stick properties
- Available in multiple arch, taper, offset and special constructions
Unalon Style 9500 PTFE Lined Metal Expansion Joints
The Unalon 9500 Series is a Metal Expansion Joint that combines the properties of metal and PTFE into an advanced and versatile joint. It features a formed PTFE liner offering enhanced chemical resistance.
- Absorbs pipe movement and stress
- Isolates mechanical vibration
- Reduces system noise
- Protects against surge forces
PTFE Lined Flexible Connectors
- PTFE and elastomeric flanges accommodate standard, metric or special drilled flange
- Beaded ends also available
PTFE Lined Metal Pump Connectors
- Smooth core PTFE liner
- Available with standard or metric flanges
- Lengths up to 50′ available
Control Units
- Control units are always recommended as an additional safety factor, preventing damage to the connector and associated equipment.
- Our experts will recommend the units appropriate for your installation
Performance Characteristics
- Chemical Resistance – mold or machined fluoroplastic connectors are used in corrosive applications due to the inherent resistance of fluoroplastic to a vast range of chemicals.
- Vibration Absorption – fluoroplastic connectors are sometimes used in HVAC applications to absorb vibration and attenuate noise.
- Temperature Limits – Fluoroplastic connectors can withstand temperatures as high as 450° F and as low as -300° F. (Temperatures significantly affect the pressure rating.)